This is the sixth posting in a blog series summarizing the new Oracle E-Business Suite 12.2 Mobile and web services functionality and recommendations for securing them.
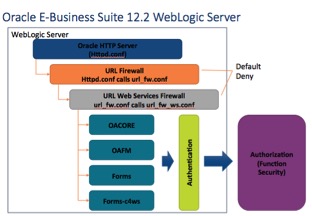
How are web services secured in Oracle 12.2? To start at the beginning, the “front door” of the Oracle E-Business Suite is its web server, the Apache server deployed within the WebLogic server that is installed with release 12.2. To secure an Apache web server largely requires setting various configurations in the Apache configuration file (httpd.conf). For the Oracle E-Business Suite, these critical settings are maintained by Oracle through the AutoConfig utility.
URL Firewall
The most important setting for Internet-facing clients is the include for the Oracle E-Business Suite’s URL Firewall. When the URL Firewall is included in the httpd.conf, every web request is passed through the URL Firewall, both for forms and for web services. The URL Firewall is non-discretionary and mandatory requirement when the Oracle E-Business Suite is deployed on the Internet.
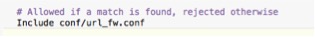
HTTPD.CONF include for the URL Firewall
The URL Firewall is a template maintained by Oracle that whitelists those forms (e.g. JSP pages) that Oracle Corporation has hardened for use on the Internet. If the JSP is not listed “whitelisted” in the file url_fw.conf it should NOT be used on the Internet. Be sure to use the latest version of the template as Oracle periodically updates the template.
In the template, Oracle comments out all lines which effectively “Denies All.” To use the url_fw.conf, DBAs at each client site need to manually uncomment (“open”) specific JSP pages appropriate to their site. This “opening” by the DBAs must be carefully done and routinely reviewed.
The mechanics of when the url_fw.conf is called or not is determined by the Node's trust level. Most large Oracle E-Business Suite implementations have multiple web servers (referred to as nodes). To deploy the Oracle E-Business Suite on the Internet, one ore more nodes are deployed in a DMZ. If the node making the request of the Apache web server is flagged as an "Internal" web node, the url_fw.conf is skipped. If however the Node's trust level is flagged as "External" because the node is deployed in the DMZ, the url_fw.conf is called.
When called, the url_fw.conf applies regular expressions to the web request to determine if the request is BOTH exists in the whitelist and has been uncommented “opened” by the DBAs. If no match is found, a default-deny result is returned. In security terms, this means all requests are rejected unless explicitly allowed. If a match is found, the web request continues and the WebLogic server will then proceed with authentication and authorization tasks.
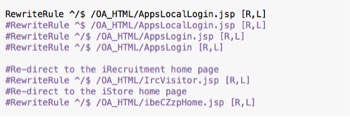
Example of URL FW line uncommented
Enabling and configuring the URL Firewall is the first step in securing web services. Unfortunately, Oracle buries the documentation for the URL Firewall in Appendix E of DMZ configuration guide – see the reference section of this paper for more information on the documentation.
To secure web services, it gets more complicated in that a second whitelist is appended to the first. To secure Oracle E-Business Suite web services, the url_fw.conf calls the url_fw_ws.conf. Similar to the configuration of the url_fw.conf, the documentation is buried deep in Appendix E of the DMZ configuration guide.
Different than the url_fw.conf which is supplied as a static listing of JSP pages, a utility (txkGenWebServiceUrlFwConf.pl) is run to generate the file url_fw_ws.conf. After being generated, DBAs similarly need to manually uncomment only those lines for the web services being used. If a web service is not found to be whitelisted, a default-deny rule will be applied; all web services commented out will be denied.
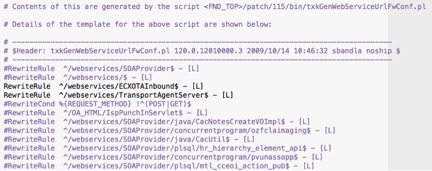
Example of URL FW WS.conf
Errors in selecting a Node’s trust level and configuring either the url_fw.conf and/or the url_fw_ws.conf have serious security consequences and should be routinely reviewed as part of on-going security audits.
Web services can be publically deployed without using the URL Firewall. For example, clients can if they so choose route Internet traffic directly to the E-Business Suite without setting up an External node. Integrigy Corporation highly recommends against doing this. Integrigy Corporation highly recommends always using the URL Firewall when deployed on the Internet, both for forms and for web services.
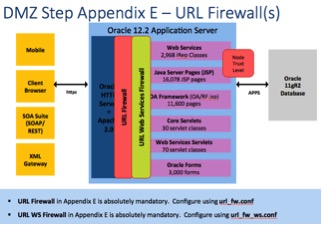
URL Firewall called by Node Trust Level
httpd.conf calls the URL Firewall
If you have any questions, please contact us at info@integrigy.com
References
- Oracle E-Business Suite Mobile and Web Services Security - Integrigy Whitepaper
- Oracle E-Business Suite Mobile and Web Services Security - Integrigy Webinar
- Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12.2 Configuration in a DMZ (Note 1375670.1)